Prepared for the Future: Policy recommendations to increase access for students to Pennsylvania's dual enrollment, early college in high school, and pre-apprenticeship programs
Major Findings:
The report titled, Prepared for the Future: Policy recommendations to increase access for students to Pennsylvania's dual enrollment, early college in high school, and pre-apprenticeship programs denotes a recurring issue in workforce research across the board. Research shows that though there are jobs that need to be filled, the upcoming talent does not possess the particular skills employers are seeking. In large part, this is because graduating university students have spent their time preparing for jobs that have existed for many years and require a static skill set. However, static skill set jobs are disappearing quickly and are unlikely to exist in the future. Instead, employers are pursuing talent who go beyond a static skill set and cultivate traits allowing for continuous learning and frequent upskilling. The research in the report shows that dual enrollment, early college in high school, and pre-apprenticeship programs can help cultivate the necessary skills and narrow the equity gap in Pennsylvania.
Dual enrollment allows K-12 students to take college courses with either college professors or their high school teachers for dual credit, where the students receive both high school and college credit. Early college in high school programs can vary in form but ultimately allow high school students the ability to graduate with their high school diploma along with either a certificate or even an associate's degree toward their post-secondary education. These students benefit from:
- Reduction in college costs
- Smoother transition to a post-secondary learning environment
- Increased academic motivation
- Higher likelihood of high school graduation into college matriculation.
- A greater chance of post-secondary success.
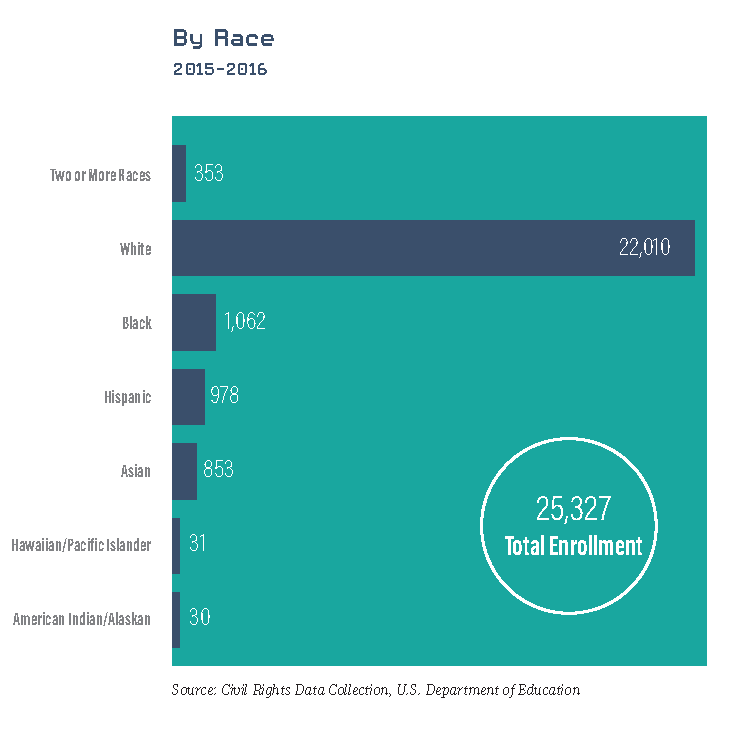
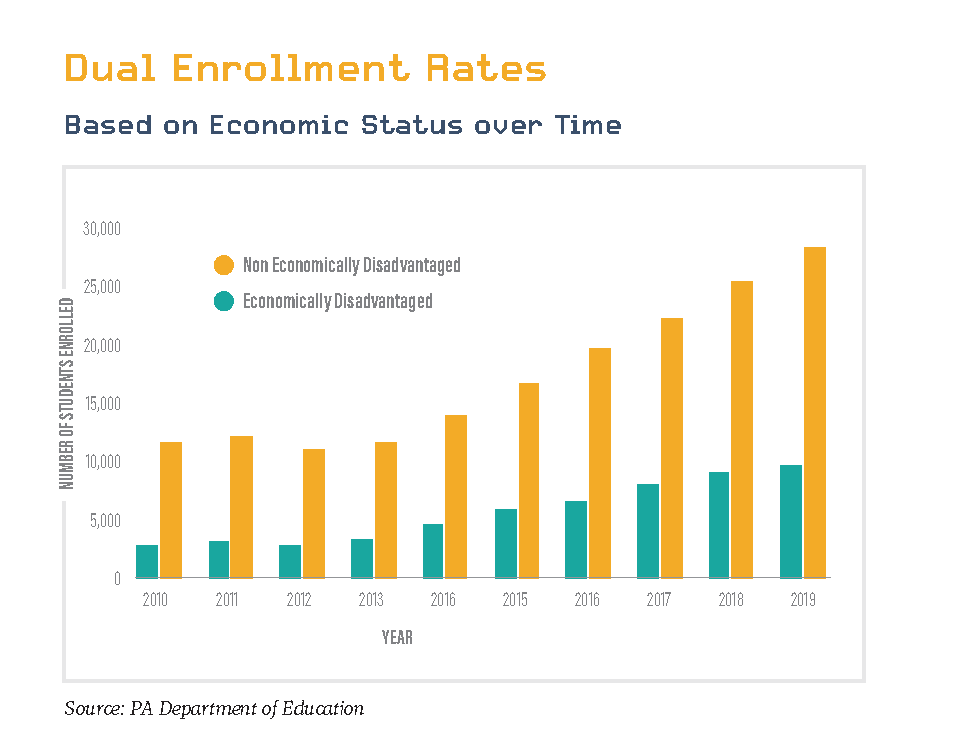
Working to recruit and retain more students of color or students from lower economic backgrounds is of paramount importance, particularly after the struggle these groups face in the post-pandemic era. One of the most effective ways of facilitating this funnel is through dual enrollment and early college in high school programs. Data from the U.S. Civil Rights Data Collection and the PA Department of Education show a significant gap in the participation of students of color in these high school programs. These programs will help foster and guide the underrepresented populations into higher education, allowing for greater diversity, inclusion, and talent funneling into the workforce in upcoming years.
Implications for Point Park University:
Though Point Park has both a college in high school and a dual enrollment program, these initiatives aren't the recruitment tool they have the potential to be. The dual enrollment and college in high school programs at Point Park University are understaffed, without consistent structure, and lack university-wide support. While working in the Center for Inclusive Excellence, one of my roles was to help facilitate the CHS program through the onboarding and articulation agreement process. At the beginning of my time at Point Park, I worked closely with the CHS and Dual Enrollment committees attending meetings, learning the processes, working alongside admissions, and reporting on new and existing articulation agreements. Throughout the Covid-19 pandemic, the CHS program fell by the wayside. There were planned attempts by the Academic Excellence Staff Committee to provide a better structure to the process, but with changes to the committee, this initiative lost traction. Several staff members currently collaborate to keep these programs functioning as best as possible, on top of their already busy work schedules. Therefore, the programs do not always receive the attention they deserve. Point Park would benefit from a small team of part-time staff members to oversee these processes. I believe this would significantly improve our recruitment, matriculation, and retention efforts.
Implications for Higher Education:
The U.S. will need an additional 20 million workers with a post-secondary degree by 2025. The demand for a more diverse and inclusive workforce is expected to continue to increase. The employer community is currently working towards investment in training to upskill employees, examine new pathways to employment for those who are underemployed, and expand internship opportunities to connect students at secondary and post-secondary levels with potential future employers. Higher education will be expected to respond in kind by investing in programs such as dual enrollment, the early college in high school, and pre-apprenticeships to best prepare the students to cultivate the soft skill set to engage in these opportunities. Beginning at the secondary education level allows the students to develop the necessary habits to engage in the upcoming workforce sector.

